Incontinence
Urinary Incontinence in men & women
Methods of treatment
Artificial sphincter – The permanent solution

Urinary incontinence in men is rarer than in women. Its frequency ranges between 12-17% in men and is divided intoThus, the urge incontinence with a non neurological cause can be usually observed in older men and is principally due to the obstruction of the outflow of the urine, due to prostatic hyperplasia. More rarely, it can be due to a tumor or stone of the urinary bladder. In younger men it is very rare, and if it suddenly occurs, the patient should be examined for some emerging neurological disease, usually multiple sclerosis.
However, the milder type of an overactive bladder, of which the stronger clinical form is the urge incontinence, is frequent urination. This phenomenon is also very frequently observed in younger men, usually due to chronic prostatitis. Overflow incontinence is sometimes observed in men with severe obstruction of the urine outflow, which is usually due to a prostatic hyperplasia. The stress urinary incontinence in men, in contrast with women, is always due to the weakness of the external mechanism of the urethral sphincter, which surrounds anatomically the section of the urethra which is located on top of the prostate. The sphincter weakness is more rarely due to neurological damages, and is usually due to surgical operations.
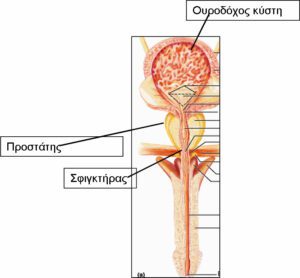
The radical prostatectomy for the treatment of prostate cancer is the most common operation that causes stress incontinence and its frequency ranges in various studies between 2%- 43%. Practically, experience shows that approximately 10% of the patients who undergo any kind of radical prostatectomy will have, 12 months after the operation, a very disturbing urinary incontinence. If we also consider that prostate cancer is the most common cancer in men, and 45 new cases out of 1000 men who are 60 years old occur per year, and that one out of six men will present prostate cancer during his lifetime, we can understand how serious the problem is. The transurethral prostatectomy for the benign prostatic hyperplasia is also relate, at a percentage of 1%-3%, with urinary incontinence. Finally, both the external and the internal radiotherapy for prostate cancer are accompanied by urinary incontinence in 1%-16% of the cases.
Urinary incontinence in men, as in women, is not a life or health threatening disease for the patient. However, it can create a serious life quality problem, with psychological effects that sometimes lead to depression. Furthermore, it is accompanied by a high cost for the purchase of incontinence diapers. Finally, due to the permanent maceration of the genital area by urine, dermatitis and mycoses are generated, which are very disturbing and difficultly treatable. Of course, if the incontinence is due to an underlying disease, the symptoms of this underlying disease coexist. For example, urinary hesitation in cases of prostatic hyperplasia.
Diagnostically and therapeutically the treatment of male urinary incontinence must be performed by the specialized urologist. In the case of urge incontinence must be controlled the possible presence of an underlying disease, the treatment of which will improve or even resolve the problem. If an underlying disease cannot be found or if its treatment did not improve the incontinence, there are medicines that can be used. In the case of overflow incontinence the obstruction must be treated, for example with an operation in case of benign prostatic hyperplasia.
The problem the specialized urologist can really help resolving, is the urinary incontinence after prostatectomy and more usually after radical prostatectomy, for the treatment of prostate cancer, as it has been mentioned before. We recommend to our patient to wait for one year after the operation, because up to then the operated tissues are still recovering and the incontinence can disappear or significantly improve and it cannot eventually disturb the patient. If this does not happen, we will examine our patient with specific special urological tests and we will propose to him the surgical treatment for his incontinence.
There are various ways to treat the urinary incontinence in men which is due to the weakness of the sphincter, and their selection is made by specialized doctors. They all include the placement of protheses. The most effective way is the placement of an artificial sphincter. This treatment is globally characterized as the “gold standard”, and the effectiveness of all other types of surgical treatment of incontinence are compared to it.
The artificial phincter is a silicone implant that consists of three sections and its function is purely hydraulic. The material is always accepted by the human organism. These sections are the cuff which is placed around the urethra, the pump and the water reservoir.The placement of the entire device is performed today through an incision that is made on the base of the penis., which is a better technique than the classical placement with two incisions.

According to the European Association of Urology, the effectiveness of the artificial sphincter is up to 60%-90%, depending on the studies, and it is the highest compared to any other operation for the treatment of incontinence after prostatectomy. The frequency of complication ranges between 4.5%-15% and in 25% of the cases the replacement of the artificial sphincter will be necessary at some point. However, the cost of the material that is going to be used in case of replacement is covered by a lifetime guarantee and is absolutely free. The National Health Insurance Fund (EOPYY) covers 90% of the cost of the material, after an approval is granded after the examination of the necessary supporting documents. The replacement, if necessary is a simple procedure in the hands of an experienced urologist.
Urge urinary incontinence due to neurological or non neurological causes

Treatment without pills. The type of incontinence that is characterized by a sudden urinating desire, that cannot be controled by the patient and is called urge incontinence, is a tormenting feeling and creates a severe social problem, as well as hygiene problems. Also, the cost of incontinence diapers is by no means inconsiderable. This kind of incontinence can be due to certain diseases. These diseases can be neurological or diseases of the bladder wall, such as inflammations or tumours.
However, in the majority of cases there is no known cause for this type of incontinence and thus it is called idiopathic. In order to exclude the presence of serious diseases, some simple medical tests, such as the ultrasound of the urinary tract, the urine test and, sometimes, the cystoscopy, must be performed.
The urodynamic test is a relatively simple examination that records the spasms of the bladder and the increase of pressure in the bladder, at the spasm phase. In the case of incontinence which is due to neurological reasons, the increase of pressure in the bladder due to the highly intense spasm causes, apart from incontinence, a reflux of the urine to the kidneys, which results to their rapid destruction and to a renal failure. The urge incontinence is treated mainly with medicines. Newer medicines, that have even less side effects compared to the older oxybutynin – that causes intense dry mouth, constipation and tachycardia -, are added to the therapeutical arsenal of the urologist.
However, the newer medicines are not totally free of side effects, and they are not always effective or tolerable. A new alternative therapeutical method for an overactive urinary bladder is the administration of botulinum toxin, with injections directly in the urinary bladder with the aid of a cystoscope. This medicine has the characteristic that it temporarily relaxes the muscular wall of the urinary bladder and can, thus, improve and, at most times, fully stop this type of incontinence.
Stress urinary incontinence – Coughing, laughing
Surgical repair within 20 minutes
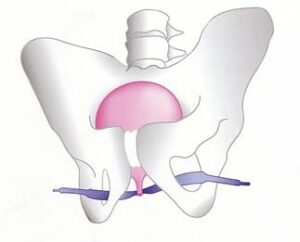
Stress incontinence is the type of incontinence which is related with the leakage of urine due to coughing, laughing, fast moving and, in general, to all situations where pressure in the abdomen area is increasing. In more severe forms, the loss of urine can be massive and can take place even during calmer activities. This type of incontinence, although it can occur in both sexes, is more frequent in women and is due to the relaxation of the muscular floor of their pelvis, usually due to atrophy of these muscles, due to childbirth and the lack of estrogens after menopause.

More rarely, this type of incontinence can be due to weakness of the continence mechanism of the sphincter, caused by neurological diseases, diabetes, or injuries of the pelvic nerves due to accidents, or more frequently after large scale operations in the pelvis for the removal of tumours. The most common type of stress urinary incontinence, that is the one that is caused by a relaxation of the pelvic floor in women, is treated with various conservative and more frequently with surgical means.
The most usual operations include the placement of tapes of polypropylene under the urethra in women. These tapes do not exercise pressure in order to block the urethra, when they are correctly placed, but act as a support of the urethra at the moment when, due to the increase of intra-abdominal pressure, the urethra moves from its position, allowing thus the leakage of urine.
These tapes are very effective in controlling incontinence and are easily placed with simple operations, with epidural or local anesthesia. They are perfectly tolerated by the human body and, very soon, they are integrated in the tissues, without any problems. These operations, in order to offer the optimal results, must be performed by specialized in incontinence urologists.
The oldest and most proven of all tapes is the TVT tape. For its placement, the two edges of this band must be pulled out of the lower abdominal wall, with the aid of special needles. Although the method is quite safe in the hands of an experienced specialist, there is still some danger of organ injury due to the use of needles.
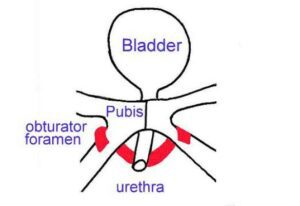
The attempts to simplify this operation has lead to two variations of the placement of the tape, by passing the tape not through the lower abdominal wall, but through the thyroid foramina in the internal surface of the thighs (TOT and TVTO tapes).
This technique reduces the duration of the operation and the danger of possible injury of the urinary bladder, the intestine and the iliac vessels. Another simplification of the TVT tape is the recently used TVT Secure tape. This tape is even more advantageous than the others due to the fact that no needles are used for the tape to pass through and, thus, its application is fast and safe, and it can be performed with local anesthesia. Its effectiveness remains to be evaluated.

